What is Spark?
Spark is an open-source cluster computing framework originally developed in the AMPLab at UC Berkeley. It is a fast and general engine for big data processing, with built-in modules for streaming, SQL, machine learning and graph processing.
Why Spark?
Spark is the First Big Data platform to integrate batch, streaming and interactive computations in a unified framework.
Compared to Hadoop’s two-stage disk-based MapReduce paradigm, Spark’s in-memory primitives provide performance up to 100 times faster for certain applications. By allowing user programs to load data into a cluster’s memory and query it repeatedly, Spark is well suited to machine learning algorithms.
Spark provides out of the box support for deploying within an existing Hadoop 1.x cluster or a Hadoop 2.0 YARN cluster.
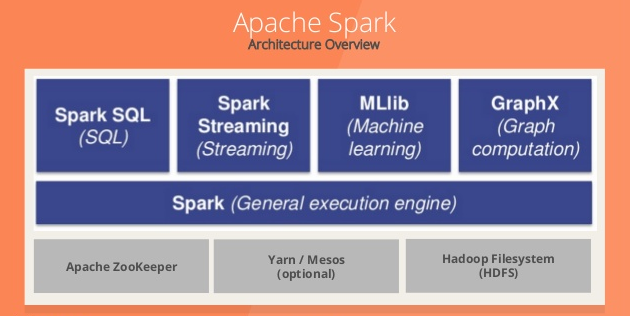
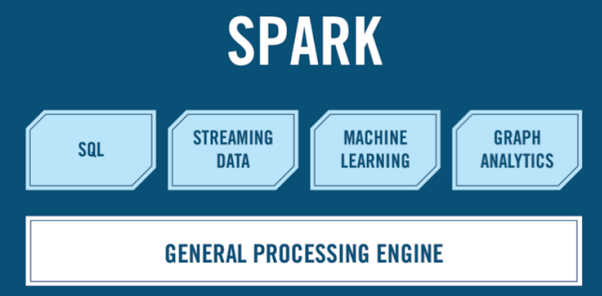
Spark Ecosystem
Spark Core is the general processing engine for the Spark platform. It provides in-memory computing capabilities to deliver fast execution of a wide variety of applications. It provides distributed task dispatching, scheduling, and basic I/O functionality. It also handles node failures and re-computes missing pieces.
Spark SQL is a SQL engine that provides the capability to expose the Spark datasets over JDBC API and allow running the SQL like queries on Spark data using traditional BI and visualization tools. Spark SQL allows the users to ETL their data from different formats it’s currently in (like JSON, Parquet, a Database), transform it, and expose it for ad-hoc/interactive querying. It also provides powerful integration with the rest of the Spark ecosystem (e.g., integrating SQL query processing with machine learning).
Spark Streaming enables powerful interactive and analytic applications across both streaming (of new data in real-time) and historical data. It readily integrates with a wide variety of popular data sources, including HDFS, Flume, Kafka, and Twitter.
MLLib is a scalable machine learning library consisting of common learning algorithms and utilities, including classification, regression, clustering, collaborative filtering, dimensionality reduction, as well as underlying optimization primitives. The library is usable in Java, Scala, and Python as part of Spark applications. According to benchmarks done by the MLlib developers, MLLib is ten times as fast as Hadoop disk-based Apache Mahout and even scales better than Vowpal Wabbit.
Spark GraphX is a distributed graph processing framework. It provides an API for expressing graph computation that can model the Pregel abstraction. GraphX includes a growing collection of graph algorithms and builders to simplify graph analytic tasks.
Spark vs Hadoop
| Spark | Hadoop |
| Distributed Compute Only | Distributed Storage + DistributedCompute |
| Generalized computation | MapReduce |
| On disk / in memory | Usually data on disk (HDFS) |
| Great at Iterative workloads(Machine learning ..etc) | Not ideal for iterative work |
| – Upto 2x – 10x faster for data ondisk- Upto 100x faster for data inmemory | Batch process |
| Java, Python, Scala supported | Java |
| Shell for ad-hoc exploration |
Generally, Spark is good for less than TB scale of data size since Hadoop might be a overkill. Spark is really great if data fits in memory (few hundred gigs). Spark is best fit for Iterative workloads (Machine learning ..etc) and streaming applications.
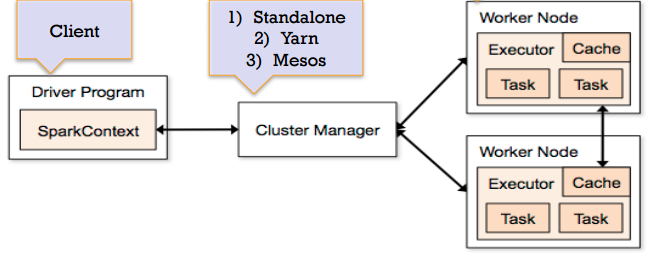
Spark architecture
Spark allows multiple ‘applications’ can run at the same time. Driver (or ‘main’) launches an application. Each application gets its own ‘executor’ and is isolated (runs in different JVMs). Data can not be shared across applications.
Spark Architecture includes following three main components:
Data Storage: Spark uses HDFS file system for data storage purposes. It works with any Hadoop compatible data source including HDFS, HBase, Cassandra, etc.
API: The API provides the application developers to create Spark based applications using a standard API interface. Spark provides API for Scala, Java, and Python programming languages.
Resource Management: Spark can be deployed as a Stand-alone server or it can be on a distributed computing framework like Mesos or YARN.
Resilient Distributed Dataset
Resilient Distributed Dataset (based on Matei’s research paper) or RDD is the core concept in Spark framework. RDD can hold any type of data. Spark stores data in RDD on different partitions. RDDs can be created by referencing datasets in external storage systems, or by applying coarse-grained transformations (e.g. map, filter, reduce, join) on existing RDDs.
RDDs help with rearranging the computations and optimizing the data processing. They are also fault tolerance because an RDD know how to recreate and recompute the datasets.
RDDs are immutable. You can modify an RDD with a transformation but the transformation returns you a new RDD whereas the original RDD remains the same.
RDD supports two types of operations:
Transformation returns a new RDD instead of a single value. Some of the Transformation functions are map, filter, flatMap, groupByKey, reduceByKey, aggregateByKey, pipe, and coalesce.
Action evaluates and returns a new value. When an Action function is called on a RDD object, all the data processing queries are computed at that time and the result value is returned. Some of the Action operations are reduce, collect, count, first, take, countByKey, and foreach.